Table of Contents
What to Expect During Pocket Reduction GUMS Surgery
Intro
Pocket reduction GUMS (Gingival and Urethral Mucosal Surgery) Procedure is a type of surgery perform to help treat periodontal disease. It is done to reduce the pocket depth that forms between the gums and the teeth. During this procedure, your dentist will use a scalpel or laser to remove the infect tissue from the affect area. This will allow your gums to heal and reattach to the tooth, reducing the pocket depth and allowing for proper oral hygiene. In this blog post, we will discuss what to expect during a pocket reduction GUMS Procedure.
Understanding Pocket Reduction Surgery
Pocket reduction surgery, also known as gingivectomy, is a surgical GUMS procedure use to treat periodontal disease. It involves removing excess gum tissue to expose more of the tooth and to reduce the depth of the periodontal pocket.
Periodontal pockets are deep crevices that form between the teeth and gums when bacteria and plaque build up on the teeth and cause inflammation. Over time, these pockets can deepen and cause tooth and bone loss.
During pocket reduction surgery, the periodontist or oral surgeon will use a scalpel or laser to remove the excess gum tissue and reshape the gum line. In some cases, they may also remove the infect tissue and bone to allow for healthy tissue regeneration.
The goal of the procedure is to reduce the depth of the periodontal pocket, making it easier to clean and prevent future bacterial buildup. This can help improve oral health and prevent tooth and bone loss.
Pocket reduction surgery is typically recommend for patients with advance periodontal disease that cannot be treat with nonsurgical therapies such as scaling and root planing. It is important to talk to your periodontist or oral surgeon about the risks and benefits of the procedure and to understand what to expect before, during, and after surgery.
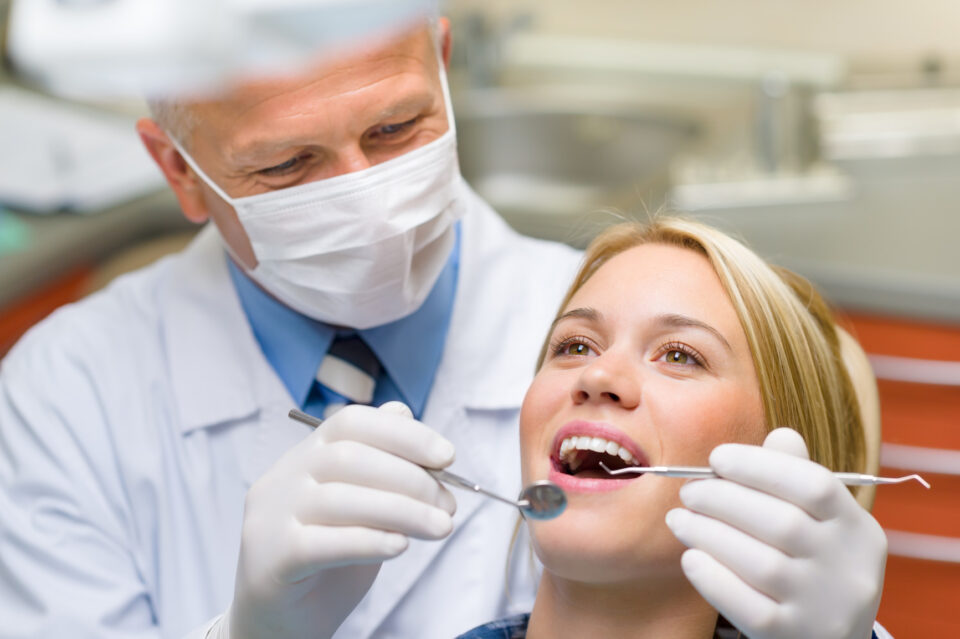
The Preparation Process
Before undergoing pocket reduction GUMS Procedure, there are a few steps that you will need to take to prepare yourself for the procedure. Firstly, you will need to schedule an initial consultation with your periodontist, who will evaluate your oral health and determine whether pocket reduction surgery is the best treatment option for your specific case.
During the consultation, you will also have the opportunity to discuss the procedure in detail with your periodontist, including any potential risks or complications that may arise, as well as the expect outcomes. Your periodontist may also request that you undergo additional tests, such as X-rays or a dental cleaning, to prepare your mouth for the procedure.
In addition, it is important to disclose any medications or supplements you are taking, as well as any medical conditions or allergies, to ensure that the anesthesia and surgical plan is tailor to your individual needs.
Finally, in the days leading up to the procedure, you may be advise to avoid smoking, alcohol, and certain foods to minimize the risk of complications during and after the surgery.
Overall, proper preparation is key to ensuring a safe and successful pocket reduction GUMS procedure, and your periodontist will work with you every step of the way to ensure a comfortable and stress-free experience.
Anesthesia Options
During pocket reduction surgery, anesthesia is use to ensure the patient’s comfort and minimize any potential pain or discomfort during the procedure. There are several anesthesia options available, and your dentist or oral surgeon will discuss which is the best for your individual needs.
Local anesthesia is the most common option for pocket reduction surgery. This involves numbing the affect area with a local anesthetic to eliminate any sensation in that region. With local anesthesia, you’ll be awake during the procedure and may feel pressure or mild discomfort, but no pain.
Sedation anesthesia, also known as twilight anesthesia, is a deeper form of anesthesia that can help you relax and stay calm during the procedure. With this type of anesthesia, you’ll be given medication through an IV that will make you drowsy but not unconscious.
General anesthesia is a less common option that is use in more complicate surgeries. This type of anesthesia puts you into a deep sleep, and you won’t feel or remember anything during the procedure. However, general anesthesia comes with a higher risk of complications and may require additional monitoring and equipment.
Regardless of which anesthesia option is chosen, it’s essential to follow your dentist or oral surgeon’s pre-operative instructions to ensure your safety and comfort during the procedure.
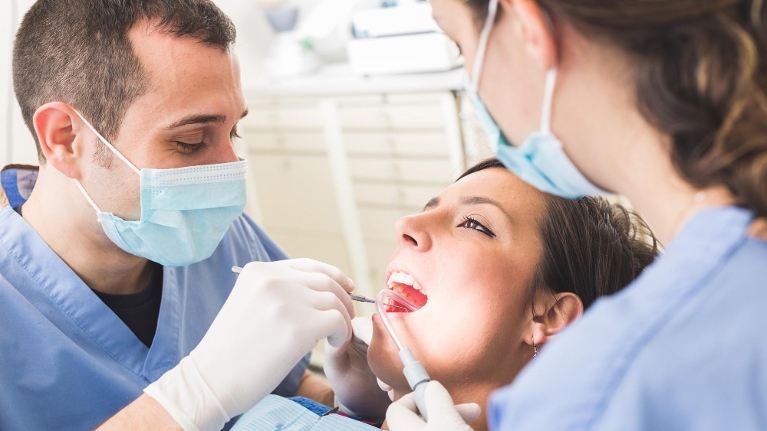
The Surgical Procedure
Pocket reduction surgery, also known as flap surgery, is a surgical procedure aim at treating gum disease by eliminating bacteria and plaque that have accumulate underneath the gumline. This procedure is usually perform after nonsurgical therapies such as scaling and root planing have been unsuccessful.
The surgery starts with the administration of local anesthesia to numb the area around the teeth and gums. After this, a small incision is made in the gums to lift them away from the teeth, creating a flap that provides the dentist or periodontist with access to the roots and bone beneath.
Once the gum tissue has been move aside, the dentist can thoroughly clean the area and remove any debris, bacteria, and tartar that has accumulate. The expose roots are then smooth out to encourage reattachment of the gums, which will eventually close up the pockets that had form due to gum disease.
In some cases, a bone graft may be perform during pocket reduction surgery to help regenerate bone that may have been damage by gum disease. After the procedure, the dentist will close the flap of gum tissue with sutures and place a bandage to protect the area and promote healing.
The surgery typically lasts around two hours, depending on the number of teeth being treat and the extent of the damage. Following the procedure, patients are advise to take it easy for a few days and follow a soft food diet until the gums have fully heal.
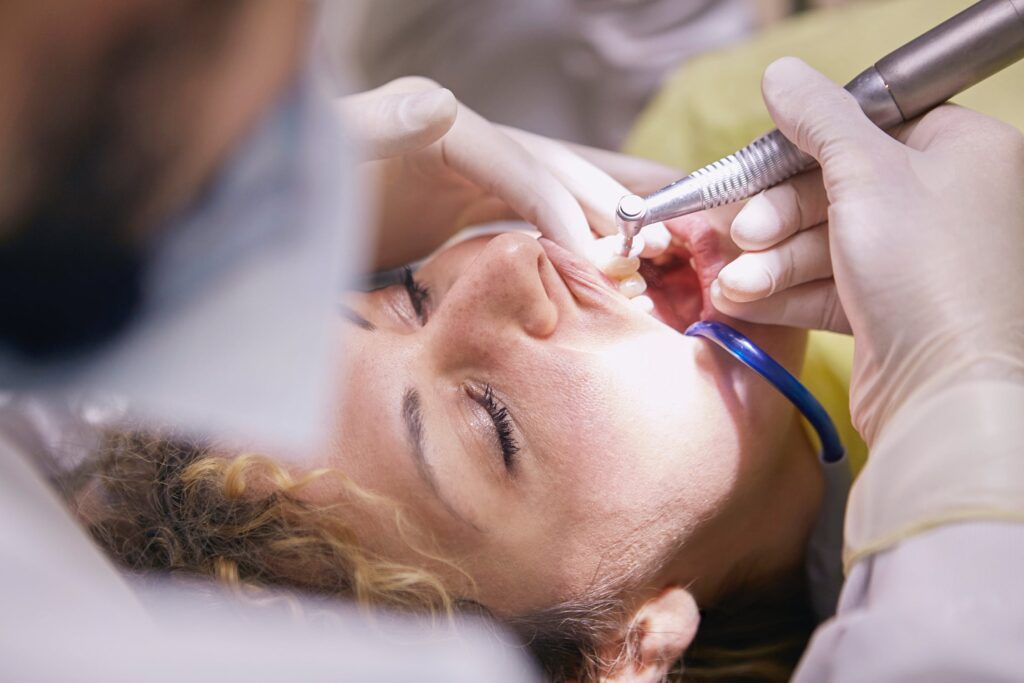
Aftercare and Recovery
After your pocket reduction surgery, your dentist or periodontist will provide you with specific instructions for your aftercare and recovery. Following these instructions will help to ensure the best possible healing outcomes. Here are some general tips to keep in mind:
– Pain Management: You may experience some discomfort or pain after your surgery. Your dentist or periodontist may prescribe pain medication or recommend over-the-counter options. Applying a cold compress to the treat area can also help reduce swelling and discomfort.
– Diet: Your dentist or periodontist may advise you to stick to a soft-food or liquid diet for the first few days after surgery. Avoiding hard, crunchy, or spicy foods can help to prevent irritation and discomfort in the surgical area.
– Oral Hygiene: It is important to maintain good oral hygiene after your surgery. However, you should avoid brushing or flossing the treat area for the first few days to allow for proper healing. Your dentist or periodontist may recommend a special mouthwash or provide specific instructions for cleaning the surgical site.
– Follow-up Visits: You will likely need to schedule a follow-up visit with your dentist or periodontist to check on your healing progress and ensure that no complications have arisen.
Remember, everyone’s recovery process is different, so it is important to follow your dentist or periodontist’s specific aftercare instructions. By taking proper care of yourself after your pocket reduction surgery, you can help to ensure a smooth and successful recovery.