Table of Contents
What are Surgical Instruments?
Surgical instruments are tools used during surgery to cut, dissect, grasp, hold, retract or suture tissue. They can be handheld or fixed in a position.
They are also used to remove fluids and slough off dead tissue. The most common types of surgical instruments are forceps, retractors, clamps and needle holders.
Types of Surgical Instruments
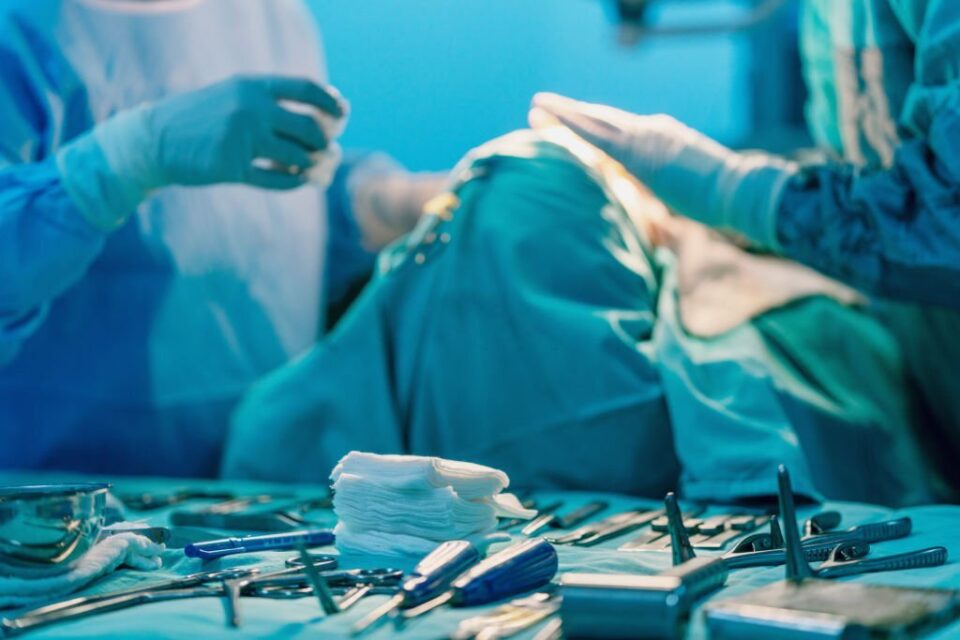
1. Surgical Scissors
Surgical scissors are used by surgeons to cut tissues within the body or on the surface of the patient. They are available in various types and styles for different surgeries.
Tenotomy scissors are small, thin scissors designed for precision cutting of delicate tissue and tiny nerves. They are used primarily in ophthalmology and neurosurgery for precise surgical dissections and transplants.
Iris scissors are used to make incisions in the iris (colored part of the eye). They come straight or curved and have a small, sharp blade.
Surgical scissors are made of stainless steel, zirconia ceramic, tungsten carbide, or nitinol. Tungsten carbide is five times harder than stainless steel, so it’s more durable and resistant to wear and tear.
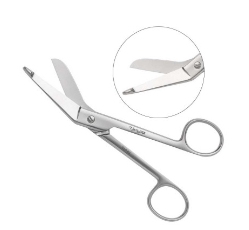
2. Surgical Forceps
Surgical forceps are a class of medical instruments that surgeons use to hold, manipulate or move tissue during surgical procedures. They can be used to pinch, lift or squeeze tissue for better view during a procedure; compress blood vessels to stop bleeding; extract human or foreign objects in the body; cut bone; and apply or remove sterile gauze.
They come with a variety of tip options to fit different applications. These include flat, ringed, cupped, serrated, teeth and grooved or diamond-dusted tips.
Teeth and serrated tip options are sometimes harmful to the tissue, but they can provide a good grip and cause less damage than a flat forceps. Smooth and cross-hatched forceps are useful for moving dressings or removing sutures.
3. Surgical Retractors
Surgical retractors are used to hold back or expose tissue, muscle, organs or bone during surgeries. These instruments help surgeons to work more efficiently, as they clear the field of view and allow the physician to see clearly.
They are divided into two broad categories: handheld retractors and self-retaining retractors. Handheld retractors require the assistance of an assistant, while self-retaining retractors are held in place by screws, ratchets or blades.
Surgical retractors are essential to surgeons, as they enable them to make surgical incisions and perform other procedures. However, they are not always ergonomically designed and pose a number of hazards to the operator. These include injury to other organs, musculoskeletal disorders and nerve damage.
4. Needle Holders
Needle holders are specialized hemostats used to grasp suture needles when performing surgical procedures. These instruments are available in many different types to meet specific physician preferences.
A common feature of needle holders is a ratchet mechanism that locks the handles together for a firm grip. Other features include comfortable finger-ring handles and jaws reinforced with tungsten carbide inserts.
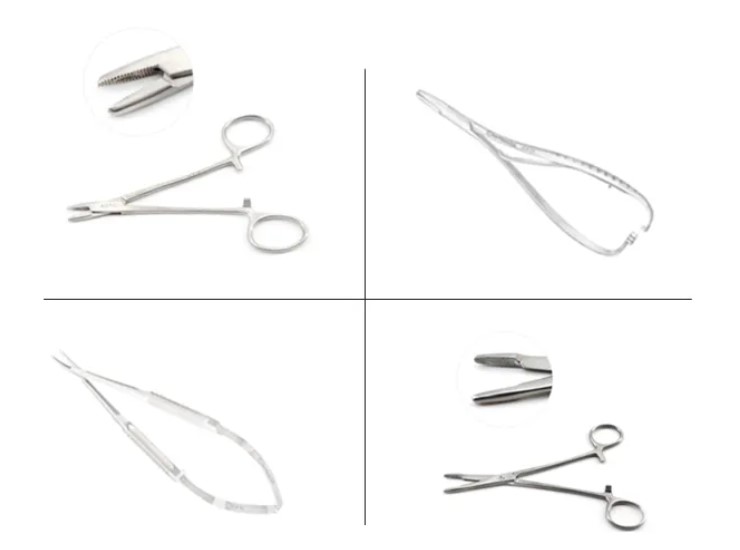
Some needle holders have serrated jaws that help hold heavy and dense suture material while providing a firm grip. These are used when heavier and stiffer sutures are needed for surgery such as tendon repairs.
A quick test to check if your needle holders are working properly is to place an appropriate sized needle in the jaws and see if you can rotate it by hand. If this is not possible, the jaws are worn or damaged.
5. Surgical Clamps
Surgical clamps are tools used by surgeons to cut off blood flow or other fluids during surgery. These instruments are used in hospital operating rooms as well as during many outpatient procedures.
There are several different types of surgical clamps. Some are small and used for laparoscopic surgery. Others are large and can be used for more precise surgical procedures.
A popular type of small clamp is the bulldog clamp, which can be applied with a thumb and forefinger or another surgical instrument such as forceps. The jaws of the bulldog clamp constrict blood vessels to stop them from bleeding during a procedure.
Hemostats are also clamping instruments. They are small ratchet-locking clamps designed to grasp or occlude blood vessels before cutting them. This is useful in cases when there are several smaller blood vessels that need to be controlled for proper surgery.
Clamps can damage both the endothelium and the media of blood vessels. Clamp injuries can occur if the clamp is not properly placed on the vessel.
Various clamps are available in different styles. For example, bone clamps have a band that can be tightened to hold bones in place, and cardiovascular clamps are used for stopping the flow of blood to an organ, such as the heart.